-
Learning for action-based scene understanding
Action plays a central role in our lives and environments, yet most Computer Vision methodsdo not explicitly model action. In this chapter we outline an action-centric framework whichspans multiple time...
-
Increasing the Runtime Speed of Case-Based Plan Recognition
We present PPC (Plan Projection and Clustering), an algorithm that creates a plan hierarchy for case-based plan recognition systems. PPC is motivated by a desire to improve the response time...
-
Image Surveillance Assistant
Security watchstanders who monitor multiple videos over long periods of time can be susceptible to information overload and fatigue. To address this, we present a configurable perception pipeline architecture, called...
-
Semi-supervised training using cooperative labeling of weakly annotated data for nodule detection in chest CT
Machine learning algorithms are best trained with large quantities of accurately annotated samples. While natural scene images can often be labeled relatively cheaply and at large scale, obtaining accurate annotations...
-
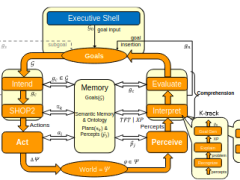
A Broad Vision for Intelligent Behavior:Perpetual Real-World Cognitive Agents
We describe ongoing work toward automating human-level behavior that pulls together much oftraditional artificial intelligence in a real-time robotic setting. Natural-language dialog, planning,perception, locomotion, commonsense reasoning, memory, and learning all...
-
Evenly cascaded convolutional networks
We introduce Evenly Cascaded convolutional Network (ECN), a neural network taking inspiration from the cascade algorithm of wavelet analysis. ECN employs two feature streams – a low-level and high-level steam....
-
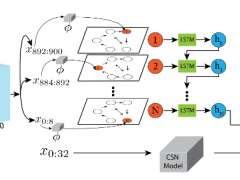
Context in Human Action Through Motion Complementarity
Motivated by Goldman’s Theory of Human Action – a framework in which action decomposes into 1) base physical movements, and 2) the context in which they occur – we propose...
-
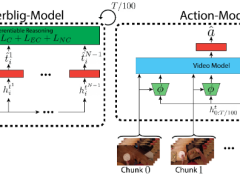
Therbligs in Action: Video Understanding Through Motion Primitives
In this paper we introduce a rule-based, compositional, and hierarchical modeling of action using Therbligs as our atoms. Introducing these atoms provides us with a consistent, expressive, contact-centered representation of...
-
Egocentric Object Manipulation Graphs
We introduce Egocentric Object Manipulation Graphs (Ego-OMG) – a novel representation for activity modeling and anticipation of near future actions integrating three components: 1) semantic temporal structure of activities, 2)...
-
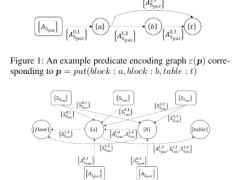
Goal-Driven Autonomy for Cognitive Systems
Complex, dynamic environments present special challenges to autonomous agents. Specifically, agents have difficulty when the world does not cooperate with design assumptions. We present an approach to autonomy that seeks...